The 'past and present' of lithium carbonate
Aug,12,24
July 21st marks the one-year anniversary of the listing of lithium carbonate futures.
Since July 21, 2023, the lithium carbonate futures market has been active, with a first day trading volume exceeding RMB 14.4 billion,
demonstrating its importance as a core raw material in the fields of new energy vehicles and energy storage.
In the early stage of listing, lithium carbonate futures prices fluctuated greatly, spot prices fell from high levels, and futures and spot prices resonated.
From the opening of 246000 yuan/ton to the end of 2023, the price dropped by 56% to 107700 yuan/ton.
In the first quarter of 2024, due to a mismatch between supply and demand, prices rebounded strongly in a short period of time,
but later returned to the downward range due to the gradual release of supply.
As of the time of publication, the average spot price of lithium carbonate has fallen below a three-year low to around 90000 yuan/ton.
The Chinese lithium carbonate industry has experienced significant growth since 2016,
with production increasing from an annual output of 78000 tons to 460000 tons by 2023, with a compound annual growth rate of 29%.
The mismatch between resource development cycle and demand cycle has led to concerns about oversupply of lithium carbonate in the past two years.
But with the rapid development of the new energy industry, the demand for lithium resources continues to grow,
and the launch of lithium carbonate futures helps companies to manage risks and discover prices.
In addition, as an important global producer and consumer of lithium carbonate,
China's physical delivery of lithium carbonate futures is expected to enhance its influence and voice in the global lithium product pricing system.
1、 What is lithium carbonate
Lithium Carbonate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li ₂ CO ∝, a molecular weight of 73.89 g/mol,
a density of 2.11 g/cm ³, and a melting point of 723 ° C.
It is a carbonate of lithium, a white crystalline powder that is soluble in water and exists in mineral form in nature,
but is mainly produced through artificial synthesis.
Lithium carbonate has a wide range of applications in battery manufacturing, glass and ceramic industries, pharmaceuticals, and other fields.
Battery manufacturing: Lithium carbonate is an important material for producing lithium-ion batteries, used in electric vehicles, grid energy storage devices,
and portable electronic devices. In the pharmaceutical field, lithium carbonate is used as a medication to treat bipolar disorder and help stabilize emotional fluctuations.
Ceramic and glass industry: used as a flux to lower melting point, improve product strength and quality.
Other applications: It is also used in industrial processes such as air purification, metallurgy, and polymers.
2、 What is lithium carbonate
The discovery and history of lithium carbonate can be roughly divided into three stages.
Early discovery: The history of lithium carbonate can be traced back to the 1800s.
In 1817, Swedish chemist Johan August Arfvesson first discovered lithium from spodumene.
Industrial application: By the mid-19th century, scientists had successfully extracted and converted lithium into lithium carbonate.
However, the industrial production of lithium carbonate did not begin until the early 20th century.
In 1916, lithium carbonate was first prepared and began to be used in medical research.
In 1949, Australian doctor John Cade first stated that lithium carbonate could be used as a drug to treat bipolar disorder, marking its application in psychiatry.
Modern development: At the end of the 20th century, with the development of lithium-ion battery technology, it became a key material in the field of new energy,
and the demand for lithium carbonate in battery manufacturing increased significantly.
Lithium ion batteries have become a widely used battery technology due to their high energy density and long lifespan, driving global demand for lithium carbonate.
3、 Distribution of lithium resources
The global distribution of lithium resources exhibits distinct regional characteristics, mainly concentrated in Australia, Chile, Argentina, China, and the United States.
Lithium resources mainly exist in the form of spodumene, lithium mica, etc., which are extracted from hard rock minerals and salt lakes.
The mining and extraction process requires high environmental and technical requirements.
Among them, Australia is the world's largest producer of hard rock lithium, with major mining areas including Greenbushes and Pilbara.
Hard rock ores have high lithium concentrations and are easy to mine and process.
Chile is the world's second-largest producer of lithium,
and the high lithium concentration brine from the Atacama Salt Lake has low recovery costs and high economic value.
In addition, Argentina has enormous potential for lithium production, with high salt lake brine resources in the main mining areas of Catamarca and Jujuy provinces,
but the harvesting process is complex.
Lithium resources in the United States are concentrated in Nevada and North Carolina,
but production is relatively small, investment is slowing down, and there is great potential for development.
The Uyuni Salt Lake in Bolivia has abundant lithium resources, but has not yet been extensively developed and is located in the South American lithium triangle region.
China is also an important producer of lithium salt products. Salt lakes in Qinghai and Xizang
and hard rock mines in Sichuan and Jiangxi integrate brine and hard rock resources,
with a high level of technological development.
4、 Production process of lithium carbonate
The production of lithium carbonate mainly involves two methods: lithium extraction from ore and lithium extraction from salt lakes.
Lithium extraction from ore is achieved through physical and chemical processing of lithium ore,
while lithium extraction from salt lakes is achieved by extracting lithium from saltwater containing lithium.
Both methods have their own advantages, but they both face challenges in terms of cost and environment.
Method 1: Extracting lithium from ore
Sulfuric acid roasting method (spodumene) and sulfuric acid roasting method (lithium mica) are two mature lithium extraction technologies for lithium ores.
Sulfuric acid treatment of spodumene concentrate is currently the most widely used lithium extraction process for ores.
The process is easy to control, and the product quality is stable and reliable.
After years of development and improvement, the process has become relatively mature.
The process steps of sulfuric acid acidification roasting method include the following steps:
Ore crushing and beneficiation: By crushing and grinding, the ore is processed into suitable particle size,
and then high-purity lithium concentrate is produced through flotation or reselection methods.
Most spodumene and lithium mica use flotation technology, which has a high recovery rate.
Roasting (including acid roasting): Roasting lithium ore at high temperatures to convert it into soluble compounds.
This process technology is mature and the output is stable,
but high-temperature roasting leads to high energy consumption and generates waste gas.
Leaching: Typically, sulfuric acid or pure water is used for leaching to form a lithium containing solution, also known as lithium sulfate solution.
The leaching rate of this step directly affects the cost, and the use of strong acid poses a risk of environmental pollution.
Impurity removal and precipitation: In order to extract pure lithium from lithium containing solutions, impurity removal and precipitation treatment are required.
Obtain lithium carbonate precipitate through neutralization, impurity removal, and filtration.
This step has high purification efficiency, but requires precise control of precipitation conditions.
Drying and packaging: Drying treatment requires temperature and humidity control to ensure the quality of the finished product.
This process is mature and easy to achieve large-scale production.
Method 2: Extracting lithium from salt lakes
The mainstream method for extracting lithium from salt lakes is "old brine extraction",
which extracts lithium from enriched old brine by extracting the original brine and treating it with sodium and potassium salt tanks.
This method utilizes high evaporation rate and low cost to enrich lithium from low grade to high grade,
but it has disadvantages such as low lithium yield, long brine cycle (12 to 24 months), the need for large-scale salt field systems,
and limited production capacity due to the scale of potassium fertilizer production.
In recent years, direct lithium extraction (DLE) technology from salt lake raw brine has made significant progress.
DLE technology directly extracts lithium from salt lake brine, saving the cost of salt field construction and brine concentration process time,
significantly improving the comprehensive yield of lithium resources, and reducing the cost of lithium carbonate.
The first phase of the century old salt lake lithium extraction project developed by Qing Shan
and the French company Eramet Group in Salta Province, Argentina, will become the first 10000 ton level DLE project.
The lithium extraction process from salt lakes is mostly based on a "one lake, one strategy" approach.
Currently, the main process routes for producing salt lakes are as follows.
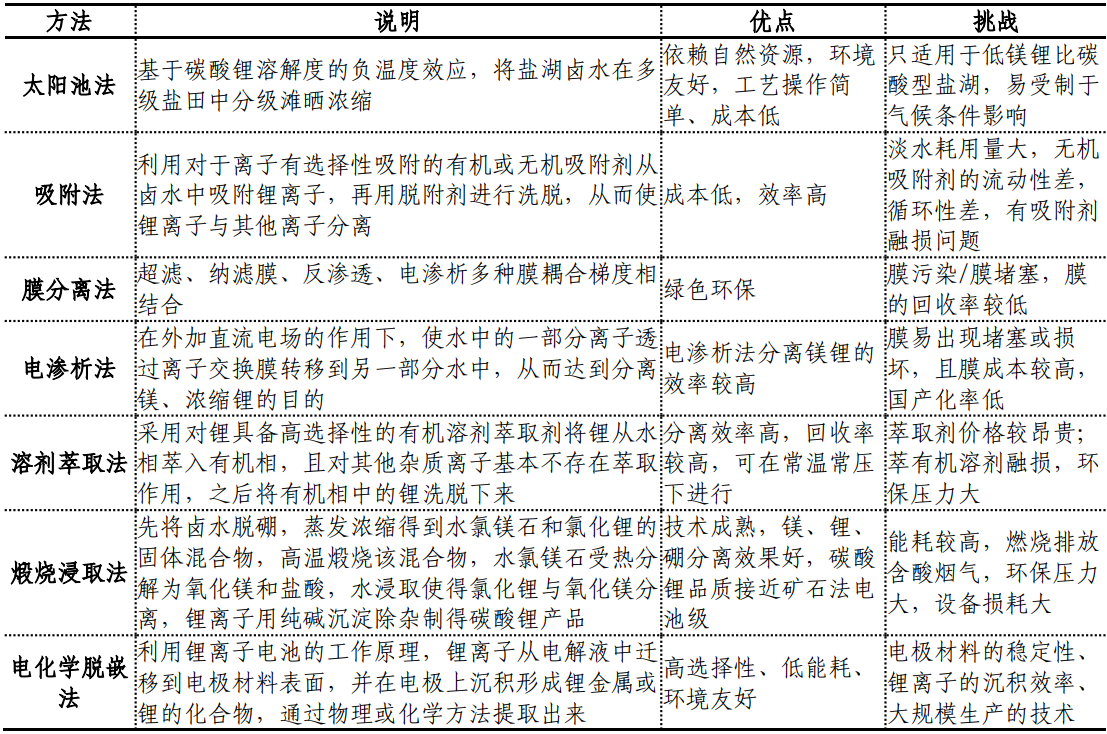
5、 The Development History of China's Lithium Industry
China's lithium industry started relatively late, but has developed rapidly.
From the initial lithium ore mining to the later salt lake lithium extraction technology,
China has made significant achievements in the development and utilization of lithium resources.
With the development of new energy vehicles and energy storage technology,
China has become one of the world's important lithium consuming countries.
The development history of China's lithium industry is rich,
from early exploration to the current major global lithium production and consumption markets,
experiencing multiple stages of change and transformation.
Initial exploration stage (1950s-1980s): mainly focused on preliminary investigation and exploration of lithium resources.
In the early 1950s, the exploration of lithium resources began.
By the 1980s, the discovery of Zabuye Salt Lake in Xizang marked the start of lithium extraction technology in China's salt lakes, laying the foundation for industrialization.
The initial stage of industrialization (1980-2000s): China officially began the industrialization attempt of lithium extraction from salt lakes,
and the lithium mineral resources in areas such as Yichun, Jiangxi were further developed.
Lithium minerals and salt lake lithium extraction technology began to be preliminarily applied in production practice,
forming a basic framework for the development and utilization of lithium resources.
Rapid development stage (2000-2010s): With the booming global electric vehicle industry, the demand for lithium has increased sharply.
Domestic enterprises such as Ganfeng Lithium and Tianqi Lithium have rapidly emerged,
and technologies for extracting lithium from ores and salt lakes have been widely applied,
resulting in an increasingly diverse range of lithium products.
Internationalization Expansion Stage (2010s-2020s): Chinese companies have accelerated their pace of overseas mergers and acquisitions,
actively participating in the development and competition of international lithium resources.
After 2015, Chinese lithium companies accelerated their overseas layout,
and Tianqi Lithium successfully acquired shares of Chile's SQM company, significantly enhancing the influence of Chinese lithium companies.
Sustainable development stage (2020s present): China's lithium industry is developing towards a more environmentally friendly and sustainable direction,
with a focus on achieving green transformation and sustainable development of the lithium industry,
contributing to global energy transformation and low-carbon development.
6、 Current situation of lithium carbonate industry
At present, the lithium carbonate industry is in a period of rapid development, gradually shifting from "industrial monosodium glutamate" to "white petroleum".
With the increasing global demand for new and clean energy, the demand for lithium carbonate is also constantly rising.
However, due to different expansion cycles, there is a mismatch between supply and demand for lithium carbonate,
and the growth rate of the supply side has not fully kept up with the growth of demand, resulting in significant fluctuations in lithium carbonate prices,
skyrocketing to 600000 yuan/ton. After 2023, with the gradual release of supply, the price of lithium carbonate will also rapidly fall,
returning to below 100000 yuan/ton by the end of 2023, and maintaining a fluctuation range of 90000 to 120000 yuan/ton in the first half of 2024.
(1) Industry Overview
Lithium carbonate is one of the important lithium compounds in modern industry, and lithium is also known as "white MSG",
widely used in fields such as batteries, glass, ceramics, lubricants, etc. With the rapid development of new energy vehicles and energy storage markets,
the demand for lithium carbonate is constantly increasing, and the application of lithium is also increasing.
In 2023, the global lithium carbonate market will continue to maintain a strong growth trend,
with China dominating the production and consumption of lithium carbonate.
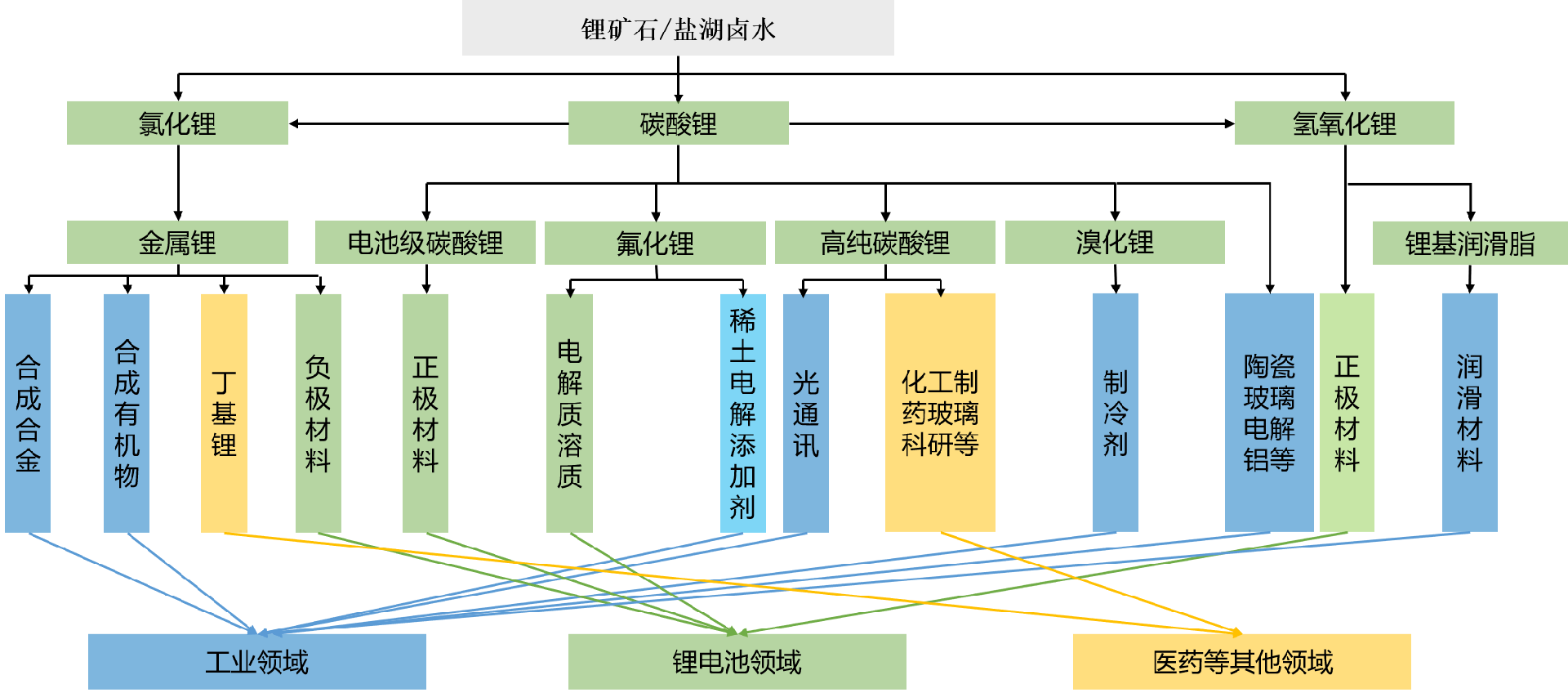
(2) Main markets
China: an important market for lithium carbonate production and consumption in the world,
with production concentrated in Qinghai, Sichuan, Jiangxi and other places.
Consumption is mainly used for battery manufacturing, especially for new energy vehicle batteries.
Australia: One of the major lithium raw material producing countries, exporting lithium carbonate raw material spodumene concentrate to countries such as China,
with lithium raw material production accounting for over 40% in 2023.
Chile: has abundant salt lake resources, high grade, and good mining conditions. SQM and Albemarle are the main producers.
7、 Operation of lithium carbonate futures
On July 21, 2023, the Guangzhou Futures Exchange listed the first physically deliverable lithium carbonate futures.
Although CME and LME successively listed lithium hydroxide futures in 2021,
their overall performance was not active due to cash delivery and few overseas participants.
Since the listing of lithium carbonate futures on the Guangzhou Futures Exchange,
the overall operation of lithium carbonate futures has been stable and orderly, with gradually increasing liquidity.
The market depth has significantly increased compared to the initial stage of listing, and it has moderate liquidity to undertake corporate risks.
According to the lithium carbonate operation report released by Guangqi Exchange in April 2024,
there is a high correlation between lithium carbonate futures and spot prices.
At present, lithium carbonate futures have formed a continuous, open, and transparent futures price,
and the correlation coefficient between futures and cash is basically maintained at around 0.98, fully highlighting the price discovery function.
In addition, the level of industry participation is gradually increasing, and the integration of current business is gradually becoming popular.
At present, the proportion of corporate clients' holdings is about 56%, and their holdings have significantly increased compared to the initial stage of listing.
Since the listing of lithium carbonate futures, the proportion of futures prices used in spot trading has steadily increased.
The domestic lithium carbonate trade model mainly includes Changxie and individual orders,
where Changxie calculates the average price and discount coefficient of one or more third-party quotations,
while individual orders are calculated in the form of third-party prices and discounts or fixed prices, resulting in low market price transparency.
According to market research, the proportion of lithium carbonate spot prices quoted in the form of futures premiums has increased from less than 5% in 2023 to 35% in May 2024.
Some lithium salt factories in the long-term agreement have also included futures prices as pricing benchmarks.
Not only is futures pricing used in spot trading of lithium carbonate, but lithium concentrates from Zimbabwe also purchase lithium carbonate futures prices as benchmarks.
The influence of China's lithium carbonate futures is gradually expanding, and the formation of international lithium pricing power has favorable conditions.
8、 Future prospects
With the global pursuit of sustainable energy, the demand for lithium carbonate is expected to continue to grow.
Technological innovation and the development of new lithium resources will help alleviate supply pressure,
but at the same time, environmental and social issues need to be addressed to ensure the sustainable development of the lithium industry.
The global demand for lithium batteries is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 20% from 2023 to 2027,
with the proportion of energy storage battery demand expected to increase from 17% in 2023 to 23% in 2027.
Specifically, there are several key points worth paying attention to.
Lithium carbonate production capacity increase:
Global lithium carbonate production capacity is expected to exceed 2 million tons of lithium carbonate equivalent by 2024,
an increase of nearly 30% compared to 2023.
Excess supply of lithium resources: SMM predicts that global lithium resources may continue to be in a state of oversupply from 2024 to 2026,
and lithium carbonate prices may face pressure.
The impact of cost and resource projects: Against the backdrop of global lithium resource oversupply,
companies that rely on outsourcing lithium concentrate may face higher costs and the risk of gradual elimination.
Price forecast: In the next 1-3 years, lithium carbonate supply may continue to be in surplus,
with prices fluctuating at the bottom and the volatility significantly reduced.
Technological progress and cost control: With the further maturity of lithium extraction technology and the development of DLE technology,
it will reduce the time required for salt lake lithium extraction projects and lower the investment cost of salt field construction.
The impact of environmental issues: The rapid expansion of lithium extraction capacity from domestic ores may increase
the cost of lithium carbonate due to the problem of disposing of smelting slag after lithium extraction;
The consumption of fresh water by extracting lithium from salt lakes may constrain the subsequent expansion of production capacity.
COFCO Futures attaches great importance to the market promotion and cultivation of lithium carbonate varieties,
continuously improving the participation enthusiasm of physical enterprises in the upstream and downstream industrial chain of lithium carbonate,
and providing various service models for industrial customers according to the actual needs of physical enterprises.
It tailors risk management plans for physical enterprises in the upstream and downstream industrial chain, guides relevant physical enterprises to use futures to manage price risks,
and continuously expands the breadth and depth of services for the real economy.





